define the term drift velocity|define drift velocity of electrons : Baguio Drift velocity is the average velocity with which electrons 'drift' in the presence of an electric field. It's the drift velocity (or drift speed) that contributes to the electric current. .
Kalamunda Markets. One of our regular City events, the Perth hills offer a fantastic weekend destination that allows the public to purchase a variety fresh produce and foods direct from producers. Outdoors. The Perth Hills is a premium destination for many outdoor activities including walking and cycling trails suitable for all fitness levels .We’re starting off with Luckyland Slots, which is actually a sister site of Chumba Casino under their parent company Virtual Gaming Worlds.It means that the two sites do share some similarities, in things like the payment methods supported and the format of the customer support available - but there are plenty of differences too.
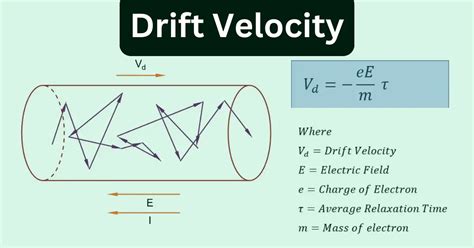
define the term drift velocity,The net velocity at which these electrons drift is known as drift velocity. Drift velocity can be defined as: The average velocity attained by charged particles, (eg. electrons) in a material due to an electric field. The SI unit of drift velocity is m/s. It is also measured in m 2 .Drift velocity is defined as the average velocity attained by the particles .Learn how to define drift velocity and derive an expression for resistivity of a conductor in terms of number density of free electrons and relaxation time. Also, find the .In physics, drift velocity is the average velocity attained by charged particles, such as electrons, in a material due to an electric field. In general, an electron in a conductor will propagate randomly at the Fermi velocity, resulting in an average velocity of zero. Applying an electric field adds to this random motion a small net flow in one direction; this is the drift. Drift velocity is proportional to current. In a resistive material, it is also proportional to the magnitu.Drift velocity is the average velocity with which, the electrons drift in the opposite direction of the field. We start with the acceleration of the electrons, a = F/m = eE/m. .Drift velocity is the average velocity with which electrons 'drift' in the presence of an electric field. It's the drift velocity (or drift speed) that contributes to the electric current. .
Subscribed. 4.4K. 162K views 3 years ago. Drift velocity is the average velocity with which electrons 'drift' in the presence of an electric field. It's the drift velocity.
Drift Velocity: Definition, Formula, and Solved Problems for Class 12, NEET, and JEE. Share the knowledge! Table of content. Drift Velocity in Conductors. Free Electrons in . Drift velocity in physics is the motion of charged particles in a material acted upon by an electric field. Charged particles experience a net velocity in one direction.define drift velocity of electrons Drift velocity is defined as the net velocity of a particle that undergoes random changes in direction and speed. This concept is typically associated with free electrons moving within a conductor. .
If the same current is set up through a wire of radius 2 r, the drift velocity will be:. At room temperature, .
define the term drift velocity define drift velocity of electrons The drift speed formula shows that the drift velocity is inversely proportional to the density of charge carriers. This means that the greater the density, the lower the velocity for a given current.

Drift velocity is defined as the average velocity acquired by the free electrons in a conductor under the influence of an electric field applied across the conductor. It is denoted by v d. Current, l = neA.v d.define the term drift velocityDrift velocity: It is the velocity with which free electrons get drifted towards the positive terminal under the effect of the applied electric field. Free electrons are in continuous random motion. They undergo change in direction at each collision and the thermal velocities are randomly distributed in all directions.
The average velocity of all the free electrons in the conductor is called the drift velocity of free electrons of the conductor. W hen a conductor is connected to a source of emf an electric field is established in the conductor, such that E = V L
Drift velocity is the average velocity of the free electrons in the conductor with which they get drifted towards the positive end of the conductor under the influence of an external electric field. ii) Free electrons are in continuous random motion. They undergo change in direction at each collision and the thermal velocities are randomly .

It also undergoes frequent collisions with the stationary ions of the wire material. These two effects result in a very slow net motion (drift) of moving charged particles in the direction of the electric force. This motion is described by the drift velocity(v d). The relationship of drift velocity with current is given by \[v_d = \frac{I}{neA .
The drift velocity can be defined as the average velocity of charge carriers, such as electrons, in a conductor due to the influence of an electric field. When an electric current flows through a wire, the charge carriers experience random motion due to thermal energy. However, when an electric field is applied, the charge carriers acquire an . Define the term drift velocity. On the basis of electron drift, derive an expression for resistivity of a conductor. asked Apr 6, 2020 in Physics by Devanshi (64.9k points) current electricity; cbse; class-12 +1 vote. 1 answer (i) Define the term drift velocity . (ii) On the basis of electron drift , derive an expression for resistivity of a .Drift velocity is defined as the average velocity with which free electrons in a conductor get drifted in a direction opposite to the direction of the applied electric field. Let n be the number of free electrons per unit volume of the conductor.The small average velocity of free electrons along the direction of positive potential is called the drift velocity. Drift velocity is denoted by v d. ii) Relaxation time: The time for which an electron moves freely between two successive collisions of electron with lattice ions/atoms is called the relaxation time. Drift velocity is given by,Define the term 'drift velocity' of electrons in a current carrying conductor. Obtain the relationship between the current density and the drift velocity of electrons. Answer the following questions: i) Derive an expression for drift velocity of free electrons. ii) How does drift velocity of electrons in a metallic conductor vary with increase .Drift velocity is the average velocity with which, the electrons drift in the opposite direction of the field. We start with the acceleration of the electrons, a = F/m = eE/m. The average velocity gained, i.e. the drift velocity, due to this acceleration = a*t = eEt/m. Here, t = relaxation time, the time between two successive collisions.(a) Define the term 'drift velocity' and 'relaxation time' giving their physical significance. (b) A conductor of length L is connected across a DC source of emf E. If the conductor is replaced by another of the same material and area of cross-section but length 5L, by what factor will be the drift velocity change? 1. Drift velocity is defined as the average velocity which the electrons are drifted towards the positive terminal under the effect of applied electric field. Vd=− eEτ m − e E τ m. Define the term drift velocity. Drift is the slow movement of an object toward something. The Average-Velocity attained by the charged particles in a material due to the influence of the electric field is known as the Drift Velocity. Drift Velocity is directly proportional to current. It is also directly proportional to the magnitude of the external electric field in a . Strategy. We can calculate the drift velocity using the equation I = nqAvd. The current I = 20.0A is given, and q = − 1.60 × 10 − 19C is the charge of an electron. We can calculate the area of a cross-section of the wire using the formula A = πr2, where r is one-half the given diameter, 2.053 mm.The small average velocity of free electrons along the direction of positive potential is called the drift velocity. Drift velocity is denoted by v d. ii) Relaxation time: The time for which an electron moves freely between two successive collisions of electron with lattice ions/atoms is called the relaxation time. Drift velocity is given by,
define the term drift velocity|define drift velocity of electrons
PH0 · relation between current and drift velocity
PH1 · formula of drift velocity
PH2 · explain the term drift velocity
PH3 · drift velocity class 12
PH4 · derive an expression for drift velocity
PH5 · define drift velocity of electrons
PH6 · define drift velocity class 12
PH7 · concept of drift velocity
PH8 · Iba pa